Rate this article :
5/5 | 1 opinion
This article was useful to you ?
Yes
No
Vous avez noté 0 étoile(s)
Sommaire
Procédure
Log files (also known as cookie files or error logs) are files that record certain types of events with a certain level of detail. Apache error log files record any error events encountered by Apache (and therefore PHP) during a visit to your website, along with details of the error encountered.
Log files are therefore a crucial tool for better understanding an error situation by making more details available. In this article, we'll look at how to display Apache and PHP error logs in your cPanel hosting.
You can view the Apache error log by following the steps below:
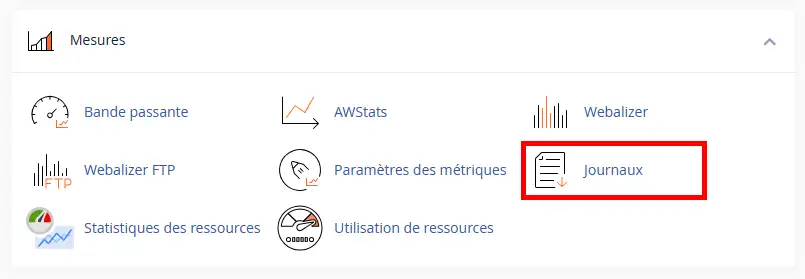
3. In the"Site log files" section (1), select the"Error log" button (2) :
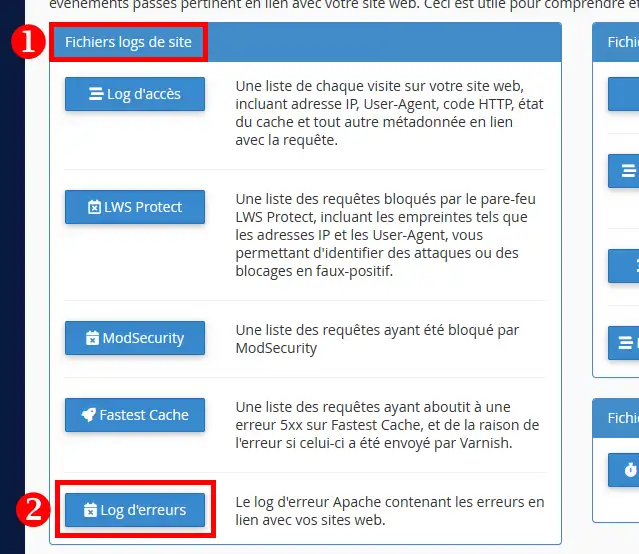
4. A list of available log files is displayed with their respective archiving dates if applicable. Click on the"View" button corresponding to the log file you wish to view:

5. The last 300 lines of the log file are then displayed:
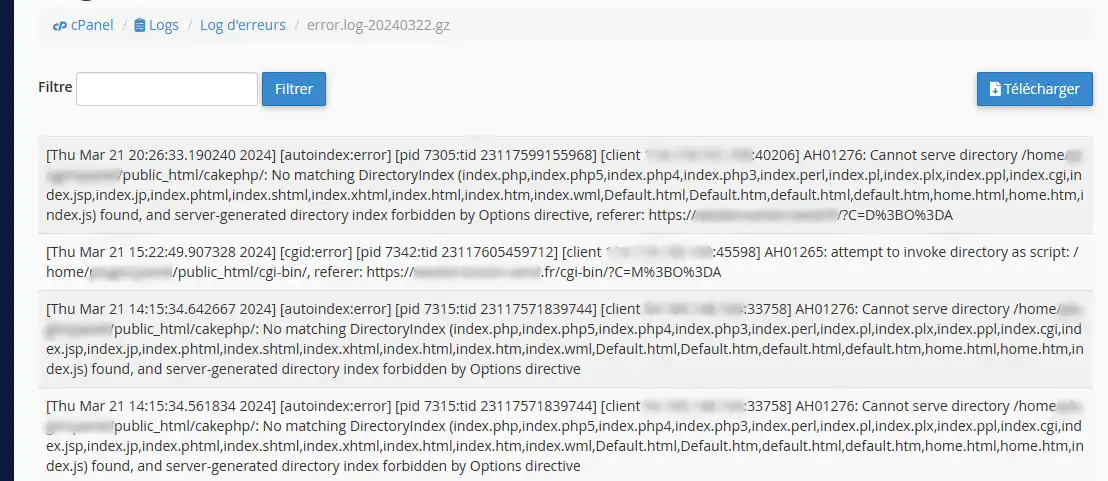
You can use the Filter field to filter the list, or use the Download button to download the entire log file.
By default, PHP errors are sent to and logged in the Apache error log file. This behaviour is reproduced thanks to the absence of content in the error_log parameter of your php.ini configuration.
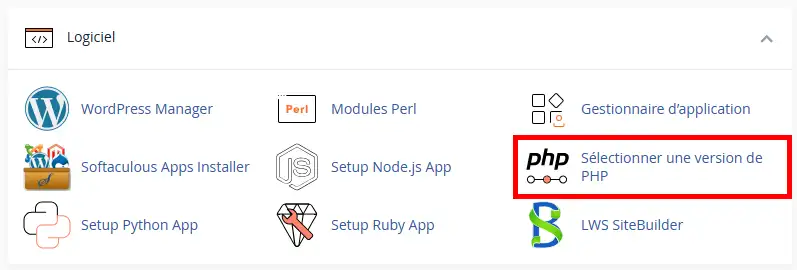
However, if you wish to log your PHP errors elsewhere, you can customise this php.ini parameter. To do this, click on the"Select a PHP version" icon on your cPanel interface ("Software" section) :
Click on the"Options" tab to access the php.ini parameters and select the PHP version concerned (if the website to be debugged uses a different PHP version by modifying the .htaccess file):
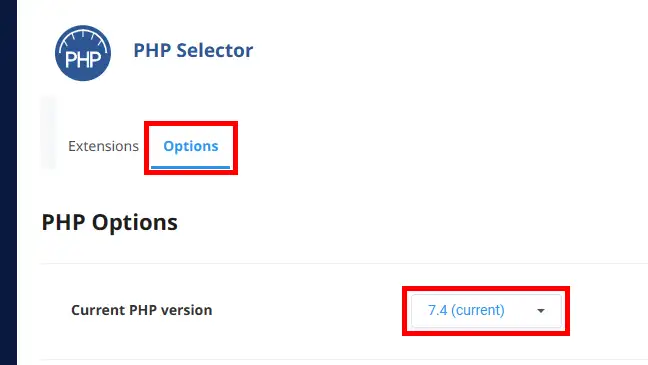
Look for the error_log option and specify a file path to store your errors:

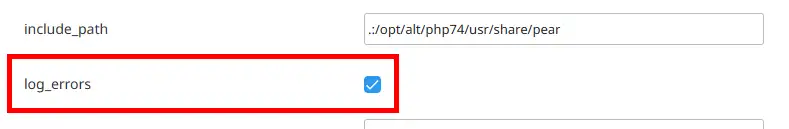
Make sure that the log_errors checkbox is enabled so that PHP uses the specified file to write logs:
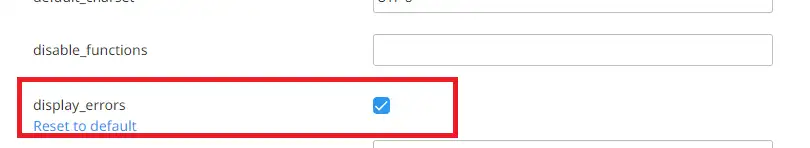
You can also check the"display_errors" box to display errors directly on your web browser (be careful, error messages may contain sensitive information such as passwords or the names of your MySQL databases):
You can readjust the error_reporting parameter to filter the error levels to be displayed:

See details on PHP error levels.
If the path of your error_log file does not begin with a "/", then the path is relative to the CWD (Current Working Directory) of the PHP process running it. With cPanel's HTTP environment, this refers to the directory that contains the PHP file being executed by LSAPI.
For example
For ease of use, always use an absolute path.
If the path of your error_log file points to /dev/null, then the log file will not be created. /dev/null is a "magic" file on Linux that allows you to forget any entry given to it.
In the interests of security, it is preferable to place the error log file in a folder that is inaccessible to visitors (apart from public_html) to prevent private information such as the name of your database that might appear in the logs from being revealed. Similarly, we strongly advise you not to allow PHP errors to be displayed to your visitors.
To view the PHP error log you have just configured, from the File Manager tool in your cPanel :
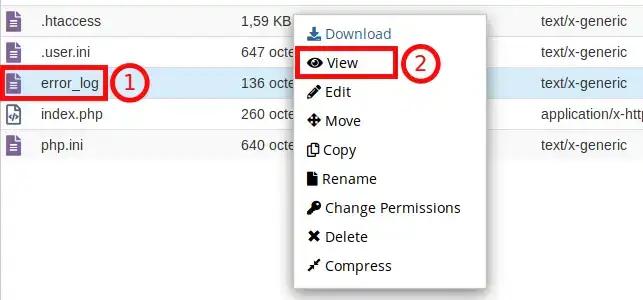
In the file, you will see each error that has been logged on a separate line. First, it lists the date and time the error was produced, then the actual error. Periodically reviewing this information will help you provide the best possible experience for your visitors to ensure that they don't see repeated errors on your website.
In this article, you've learned how to view your hosting's Apache/PHP logs, you can use this tool to detect suspicious activity via the Apache log or repair PHP errors related to your website by viewing the PHP error file.
Rate this article :
5/5 | 1 opinion
This article was useful to you ?
Yes
No
3mn reading
Wordpress on cPanel: Solving the white page or 500 error problem
1mn reading
Diagnose and correct a 500 error on a site hosted on cPanel
0mn reading
How do I correct a 403 Forbidden error on cPanel?
0mn reading
How do I correct a 404 error on cPanel?